Restriction Endonucleases From the Yeasen FuniCut™ Series, 5 minutes Digestion With Universal Buffer
Molecular cloning is used in nearly every laboratory. Restriction endonucleases are a crucial component in molecular cloning experiments, but people are also often bothered by various problems with restriction endonucleases experiments. Common problems are as follows:
- There are so many types of restriction endonucleases, it is difficult to choose.
- Miscleavage, random cleavage, or incomplete enzymatic cleavage.
- The rate of digestion is sluggish; it may take one hour or even overnight.
- Additionally, Multiple enzyme digestion experiments also need to choose a variety of enzyme digestion bTo
To prove with ide you a more thorough grasp of restriction endonucleases, the following will briefly explain what restriction endonucleases are and how various endonucleases are classified in answer to the first question. The Yeasen FuniCut™ series of Fast Restriction Endonucleases may readily resolve the second through fourth problems through strain modulation and an improved procedure!
1. What is Restriction Endonuclease?
2. Restrictions endonuclease nomenclature
3. Restrictions on endonuclease classification
4. Yeasen FuniCut™ Fast Restriction Endonucleases
1. What is Restriction Endonuclease?
Restriction endonucleases are a class of enzymes that can recognize specific nucleotide sequences in double-stranded DNA molecules and cut phosphodiester linkage in DNA chains at specific sites.
Different restriction endonucleases will recognize different DNA sequences, They can cut DNA inside the recognition sequence or at a place not far from the recognition sequence, resulting in various products, as illustrated in Figure 1. BamHI forms sticky ends, KpnI forms 3'ticky ends, and EcoRV forms blunt ends.
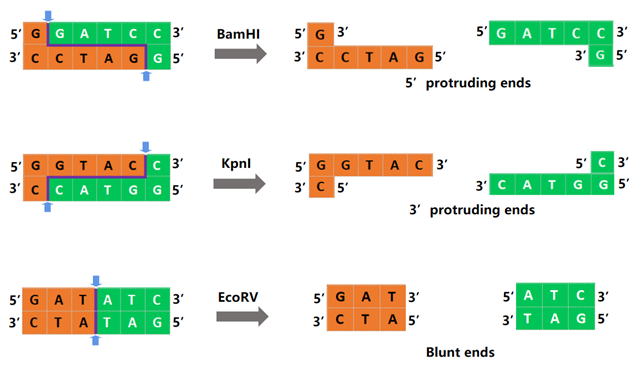
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of BamHI, KpnI, EcoRV digestion
2. Restrictions endonuclease nomenclature
The genus name, species name, bacterial strain or serotype, and the order of discovery are the primary factors used to name restriction endonucleases. The name guidelines are displayed in Table 1 below using BstEII as an example:
Table 1. Restrictions endonuclease nomenclature
|
Abbreviation |
Full Name |
Implication |
|
B |
Bacillus |
First letter of genus name |
|
st |
stearothermophilus |
The first two letters of the species name |
|
E |
ET |
The first letter of the strain name |
|
II |
Second discovery |
The order found in such bacteria |
3. Restrictions on endonuclease classification
According to the complexity of the structure, the mode, of action and the difference between the cofactors, restriction enzymes can be divided into four categories. The following table 2 summarizes the characteristics and typical enzymes of each category.
Table 2. The variations among several restriction endonucleases
|
Endonuclease class |
Features |
Typical enzyme species |
|
Type I |
1. Recognition and modification cleavage. 2. It can recognize specific DNA sequences, and the digestion site is indefinitely away from the recognition site, up to thousands of bases. 3. Action necessitates ATP. |
EcoB, EcoK, etc. |
|
Type II |
1. Only has the function of identifying cutting. 2. The recognition sequence is often a short Palindromic sequence (about 4–8 bp), and the specific digestion site of the restriction endonuclease is typically the recognized sequence. 3. Action necessitates Mg2+. 4. The type of restriction enzymes most frequently utilized in molecular cloning. |
HindIII, NotI, etc. |
|
Type III |
1. Recognition and modification digestion. 2. Aboutseparatesp separate the recognition site from the digestion site. 3. Action necessitates ATP. |
HinfIII et al. |
|
Type IV |
1. Cuts only methylated DNA sequences. 2. About 30 bp separate the recognition site from the digestion site. |
McrA, McrBC, etc. |
As indicated in Table 3 below, it may also be split into three groups based on the similarities and differences between the recognition and digestion sites.
Table 3. Comparative analysis of Isoschizomer, Neoschizomer, and Isocaudarner
|
|
Isoschizomer |
Neoschizomer |
Isocaudarner |
|
recognition sequence |
same |
same |
different |
|
digestion sites |
same |
different |
same |
|
typical representative |
AgeI and BshTI: both recognize and cleave 5′-A↓CCGGT-3′ |
SmaI (5′-CCC↓GGG-3′) and XmaI(5′-C↓CCGGG-3′) |
BamHI (5'-G↓GATCC-3') and BglII (5'-A↓GATCT-3') |
In view of the fact that some restriction endonucleases on the market still require overnight digestion, and the products are prone to incorrect digestion, Yeasen Fast Restriction Endoa nuclease, a universal buffer, complete accurate digestion in 5 minutes, allowing your digestion experiments no more troubles!
4. Yeasen FuniCut™ Fast Restriction Endonucleases
Figure 2. Yeasen FuniCut™ Fast Restriction Endonucleases
4.1 Features
- Rapid digestion: the digestion can be finished in 5–15 minutes, which can be reduced by more than 1-2 hours compared with conventional digestion experiments.
- Universal buffer: The multi-enzyme cleavage reaction is made simpler by the fact that any combination of endonucleases can use the same buffer.
- Effect of enzyme digestion: comparable to N* and appropriate for its buffer.
- Direct electrophoresis makes the process simpler by providing a red color buffer and allowing the digestion products to be delivered directly for electrophoresis.
- Precise digestion: Even with overnight digestion, there is very little star activity.
4.2 Exhibition of performance
4.2.1 In FuniCut™ Buffer, single, double, and triple digestion takes place in 5 minutes.

Figure 3. Single, double, and triple digestion using the FuniCut™ Buffer can typically be finished in 5 minutes, for example, the triple digestion using EcoRI+KpnI+SmaI.
4.2.2 The impact of the enzyme digestion is comparable to that of N* and T*, and it works well with their buffers.
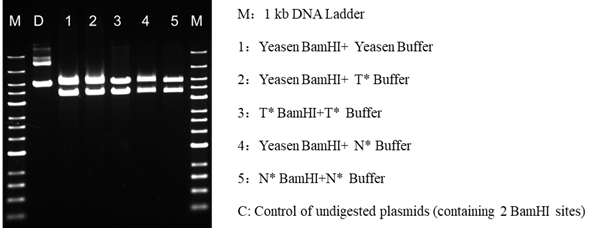
Figure 4. Compared to similar N*, T* goods, Yeasen FuniCut™ BamHI enzyme digesting effect is compatible with N*, T* brand buffers.
4.2.3 Overnight digestion with very low star activity
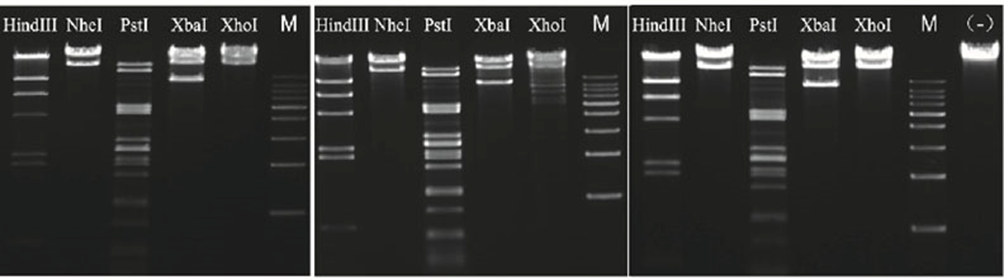
Figure 5. Utilize the rapid endonucleases HindIII, NheI, PstI, XbaI, and XhoI from the Yeasen, Tbydance with the experimental protocol advised by each brand. Perform an overnight (16 h) digestion and analyze the digested products using agarose gel electrophoresis.
4.2.4 Highly redundant and capable of handling some surplus substrate.
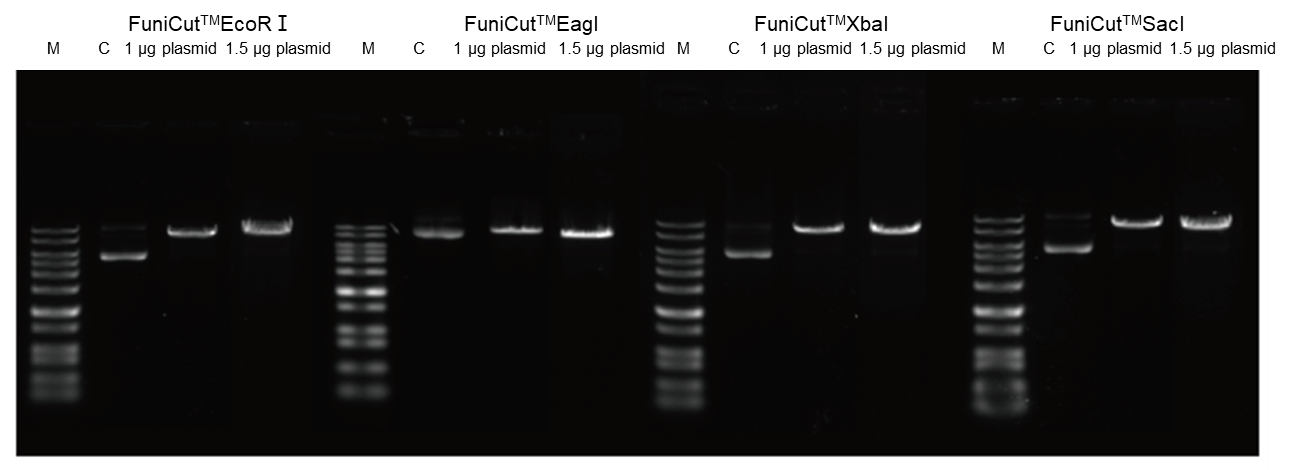
Figure 6. Using FuniCut™ Fast Restriction Endonucleases EcoR I, Eag I, XbaI, and Sac I, 1 μg and 1.5 μg of plasmid were used as substrates, respectively, and digested for 5 min, and the digested products were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis.
Table 4. Products and Reaction Buffer Compatibility
|
Product name |
Cat# |
Recognition sequence |
Temperature |
Thermal deactivation temperature |
|
T* Buffer |
N* Buffer |
Ta* Buffer |
Protected base (bp) |
Responses |
|
FuniCut™ AscI (inquire) |
15001ES50 |
GG/CGCGCC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
1 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ AvrII (inquire) |
15002ES25 |
C/CTAGG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
25T |
|
FuniCut™ BamHI (inquire) |
15003ES76 |
G/GATCC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
500T |
|
FuniCut™ BclI (inquire) |
15004ES62 |
T/GATCA |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
125T |
|
FuniCut™ BsaI (inquire) |
15005ES50 |
GGTCTC(1/5) |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Not |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ BstEII (inquire) |
15006ES60 |
G/GTNACC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
75 |
100 |
75 |
Not |
100T |
|
FuniCut™ ClaI (inquire) |
15007ES50 |
AT/CGAT |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
4 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ DpnII (inquire) |
15008ES50 |
/GATC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
75 |
100 |
75 |
Not |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ EagI (inquire) |
15009ES25 |
C/GGCCG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
25T |
|
FuniCut™ EcoRI (inquire) |
15010ES78 |
G/AATTC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
5 |
600T |
|
FuniCut™ EcoRV (inquire) |
15011ES70 |
GAT/ATC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
5 |
200T |
|
FuniCut™ HindIII (inquire) |
15012ES76 |
A/AGCTT |
37 |
80 |
100 |
75 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
500T |
|
FuniCut™ HpaI (inquire) |
15013ES50 |
GTT/AAC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
50 |
1 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ KpnI (inquire) |
15015ES70 |
GGTAC/C |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
200T |
|
FuniCut™ MluI (inquire) |
15016ES60 |
A/CGCGT |
37 |
80 |
100 |
75 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
100T |
|
FuniCut™ NcoI (inquire) |
15018ES30 |
C/CATGG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
30T |
|
FuniCut™ NdeI (inquire) |
15019ES70 |
CA/TATG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
200T |
|
FuniCut™ NheI (inquire) |
15020ES30 |
G/CTAGC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
30T |
|
FuniCut™ NotI (inquire) |
15021ES50 |
GC/GGCCGC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ PstI (inquire) |
15022ES76 |
CTGCA/G |
37 |
No |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
500T |
|
FuniCut™ SacI (inquire) |
15023ES60 |
GAGCT/C |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
100T |
|
FuniCut™ SalI (inquire) |
15024ES70 |
G/TCGAC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
200T |
|
FuniCut™ SbfI (inquire) |
15025ES25 |
CCTGCA/GG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
25T |
|
FuniCut™ SmaI (inquire) |
15027ES60 |
CCC/GGG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
1 |
100T |
|
FuniCut™ Spel (inquire) |
15028ES50 |
A/CTAGT |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ SphI (inquire) |
15029ES50 |
GCATG/C |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
1 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ SspI (inquire) |
15030ES56 |
AAT/ATT |
37 |
80 |
100 |
50 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
60T |
|
FuniCut™ StuI (inquire) |
15031ES60 |
AGG/CCT |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
1 |
100T |
|
FuniCut™ TaqI (inquire) |
15032ES70 |
T/CGA |
65 |
No |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
4 |
200T |
|
FuniCut™ XbaI (inquire) |
15033ES76 |
T/CTAGA |
37 |
80 |
100 |
50 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
500T |
|
FuniCut™ XhoI (inquire) |
15034ES76 |
C/TCGAG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
4 |
500T |
|
FuniCut™ FspI (inquire) |
15036ES50 |
TGC/GCA |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ HinfI (inquire) |
15038ES76 |
G/ANTC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
50 |
2 |
500T |
|
FuniCut™ ApaLI (inquire) |
15039ES70 |
G/TGCAC |
37 |
80 |
100 |
75 |
100 |
100 |
4 |
200T |
|
FuniCut™ NruI (inquire) |
15040ES50 |
TCG/CGA |
37 |
No |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
5 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ PacI (inquire) |
15041ES25 |
TTAAT/TAA |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
25T |
|
FuniCut™ PvuII (inquire) |
15042ES70 |
CAG/CTG |
37 |
No |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
4 |
200T |
|
FuniCut™ SacII (inquire) |
15043ES50 |
CCGC/GG |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
4 |
50T |
|
FuniCut™ NsiI (inquire) |
15044ES25 |
ATGCA/T |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
3 |
25T |
|
FuniCut™ Esp3I (BsmBI) (inquire) |
15048ES30 |
CGTCTC(1/5) |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
5 |
30T |
|
FuniCut™ BglII (inquire) |
15049ES60 |
A/GATCT |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
50 |
2 |
100T |
|
FuniCut™ BstBI (inquire) |
15050ES60 |
TT/CGAA |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Not |
100T |
|
FuniCut™ MnlI (inquire) |
15051ES50 |
CCTC(7/6) |
37 |
80 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
2 |
50T |
CpG: Affected by CpG methylation.
EK: Affected by EcoKI methylation.
EB: Affected by EcoBI methylation.
Dcm: Affected by Dcm methylation.
Dam: Affected by Dam methylation.

