PCR methodology for accurate point mutation detection – ARMS
As medical research continues to advance, targeted therapy has become more mature. The premise of targeted treatment is to do genetic testing on the molecular targets of medications to identify gene mutations that cause hereditary disorders or malignancies. ARMS-PCR is a novel method based on PCR that can detect numerous DNA point mutations. Currently, it is one of the most essential and widespread methods for the customized genetic identification of cancers. The benefits of its therapeutic use have been well acknowledged by field experts.
1. How does allele-specific PCR work?
2. How to improve ARMS specificity?
3. What are the features of products provided by Yeasen?
4. What are product performance data?
5. How do people order products?
1. How does allele-specific PCR work?
ARMS-PCR is Amplification Refractory Mutation System PCR (ARMS-PCR), also known as Allele-Specific PCR (AS-PCR). The allele-specific extension is regulated to identify the wild-type allele and the mutant wild-type gene, and the fluorescence signal value is measured using the Taqman probe technique.
ARMS PCR primers are designed with different nucleotides at the 3' end of the two upstream primers of the allele, and the two primers are, respectively, specific for the wild type and the mutant type. During amplification, upstream primers that do not completely match the template are unable to form complementary base pairs, resulting in mismatches, hindered extension, and the inability to generate PCR products, whereas primer systems that match the template can amplify the corresponding PCR products. The fluorophore on the Taqman probe may emit a fluorescent signal that can be detected by the device, and the genotype can be validated by evaluating the fluorescence data.
ARMS technology has high sensitivity, the detection limit can reach 100 copies/mL, and the detection limit for tumor tissue can reach a 0.5% mutation rate. In addition, ARMS is time-consuming and low-cost, and the results are intuitive and easy to judge. This is because ARMS combined with qPCR or electrophoresis technology requires only one PCR reaction, which takes less time. Only upstream primers need to be optimized for ARMS technology, which has lower cost and intuitive results compared to real-time PCR technology using MGB probes. Since most of the DNA extracted from paraffin-embedded tissue specimens is fragmented, accurate detection results cannot be obtained. The ARMS method is designed to minimize the length of the target product, thereby addressing this difficulty in paraffin-embedded tissue. At the same time, the ARMS combined with the PCR platform realizes closed-tube operation, which is simple to operate and does not require product post-processing, thus avoiding the contamination of amplification products to the greatest extent.
Theoretically, Taq DNA polymerase must be fully complementary to the remaining template at the 3' end of the primer to carry out efficient polymerization. However, the stringency of Taq DNA is affected by several factors. In some cases, an extension can proceed even if the 3' terminal base of the primer is not complementary to the template. If there is only one base mismatch at the 3' end, the primers can be mismatched and extended, but the extension efficiency is low. Different 3' end dislocations have different extension efficiencies. If other mismatched bases are introduced at the 3' end, the number of mismatches is too large, and the 3' end cannot be extended after a certain level. Therefore, only one base mismatch at the 3' end of the primer cannot adequately distinguish the two alleles, resulting in false positive results.
2. How to improve ARMS specificity?
The focus of improving ARMS specificity is to improve primer extension specificity. A mismatched base can be introduced at the 2nd or 3rd base from the 3' end. The mismatched bases act together with the mismatched bases at the 3' end, and in the template that is not complementary to the 3' end, the primer amplification product rate is reduced. While primers amplify normally in templates complementary to their 3' ends, the type of mismatched bases of primers depends on the type of base mismatch at the 3' end.
After the specific primers for ARMS are designed, a pair of TaqMan probes for allele-specific fluorescence resonance energy transfer is required. TaqMan probes have two fluorescent dyes, the 5' end is a fluorescent gene, and the 3' end has a general fluorescence quenching gene. In a complete probe, the quencher gene and the fluorogenic gene are spatially very close together, resulting in fluorescence quenching. Under normal circumstances, the fluorescence emitted by the fluorophore at the 5' end cannot be detected, and only the background fluorescence of the quencher at the 3' end can be detected. In the process of target gene amplification, both PCR primers and fluorescently labeled probes will be complementary to the target sequence during de-OR. When the Taq enzyme encounters a probe stably bound to the template when extending the template strand, the 5'-3' exonuclease of the Taq enzyme will degrade the specific probe bound to the template. The fluorophore on the probe is separated by physical space, the quenching effect disappears, and fluorescence is emitted. Mismatches between weakly fluorescent probes and target sequences will reduce the amount of fluorescence released.
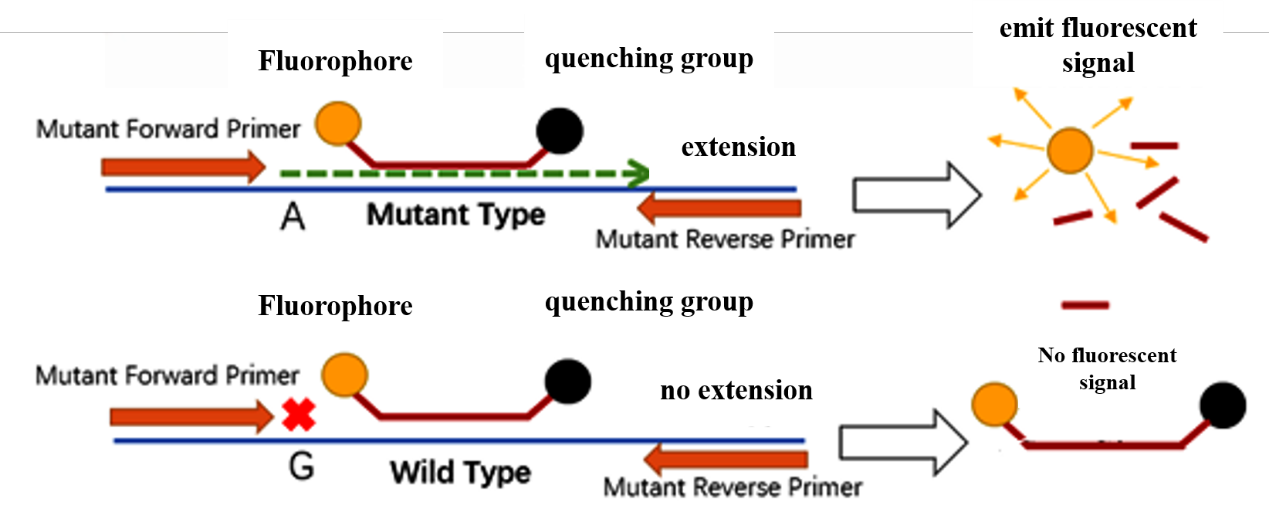
Figure 1 Fundamental concept of ARMS-PCR
3. What are the features of products provided by Yeasen?
YEASEN Hieff Unicon™ Multiplex ARMS qPCR Mix is a kit based on the amplification block concept that allows for efficient ARMS-PCR-mediated genotyping.
👍High selectivity: able to identify several gene mutations;
👍High sensitivity: mutant primers can detect mutations at concentrations as low as 0.5% in 10ng/L DNA;
👍Simple to read: The results are obvious and objectively assessed, and it is straightforward and uncomplicated;
👍Simple to operate: It is compatible with a range of PCR equipment, the mode of operation is standardized, and the on-board detection may be accomplished in 90 minutes.
4. What are product performance data?
4.1 Superior product blockage impact
Experiment: 5L of template input, 10ng/L of wild-type template, and equivalent amounts of mutant plasmid were amplified using mutant primers
Site:KRASG13D(38G>A)
Red:13755;Blue: Competitors
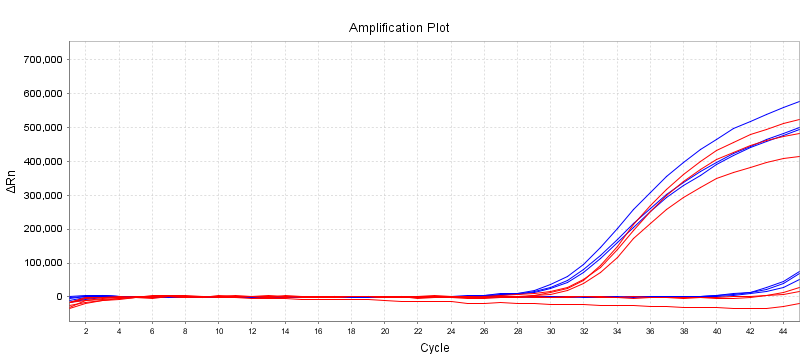
Figure 2 demonstrates that wild-type primers amplify both wild-type and mutant templates. According to the amplification curve, the wild-type template has no peak or the difference in Ct value between the wild-type and the mutant is 6-8, allowing the wild-type and mutant genes to be effectively distinguished.
4.2 The rate of product detection can reach 0.05 %
Experiment 1: Self-mixing standard preparation technique (50%): 50μL 10ng/μL wild-type DNA and 50μL 3X103 copies of mutant plasmid.
Site:KRASG13D(38G>A)
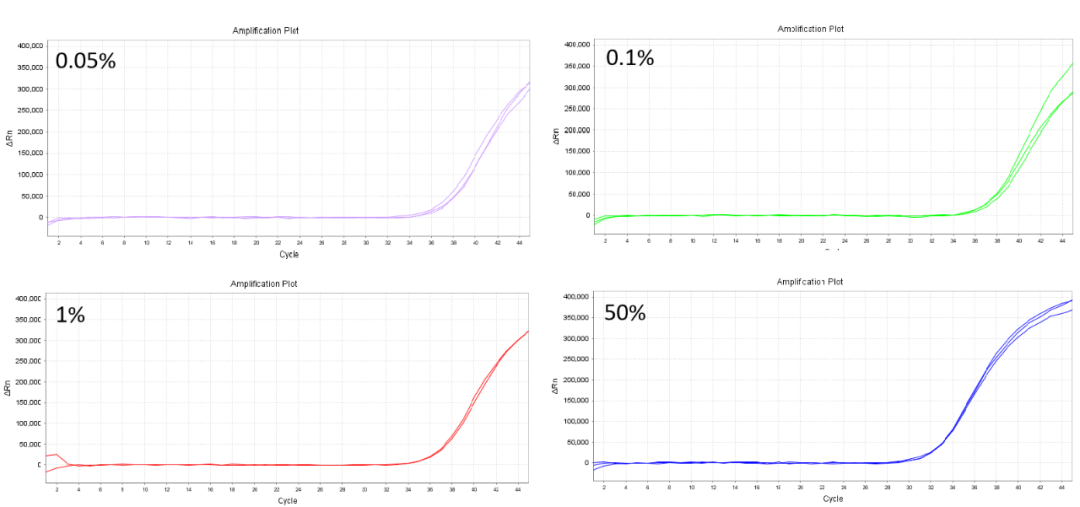
Figure 3.According to the amplification curve, the product continues to operate effectively at a concentration of 0.05 %
Experiment 2: The purchased 5% standard (50ng/μL) was diluted with library diluent to 10ng/μL, then further diluted with 10ng/μL 293g DNA to 0.1 % and 0.05 %.
Site:L858R
Red:13755;Blue: Competitors
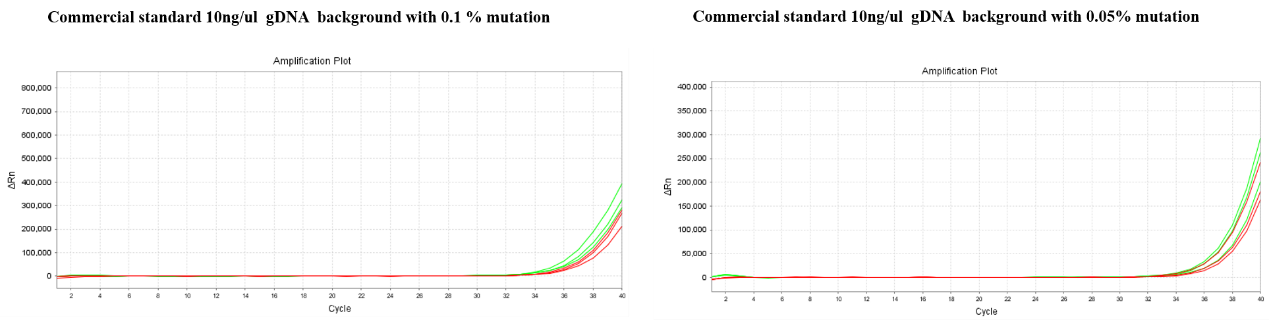
Figure 4: According to the amplification curve, the detection rate of loci against a wild-type gDNA background of 10ng/μL can be as high as 0.05%, and subsequent validation by commercial standards demonstrates that our products have an excellent detection rate.
4.3 Excellent product stability
The product's amplification and blocking effects are unaffected by 10 cycles of freezing and thawing.
Experiment: red: -20℃;green: genuine freeze-thaw 5 times; blue: genuine freeze-thaw 8 times; purple: genuine freeze-thaw 10 times.
Site:L858R
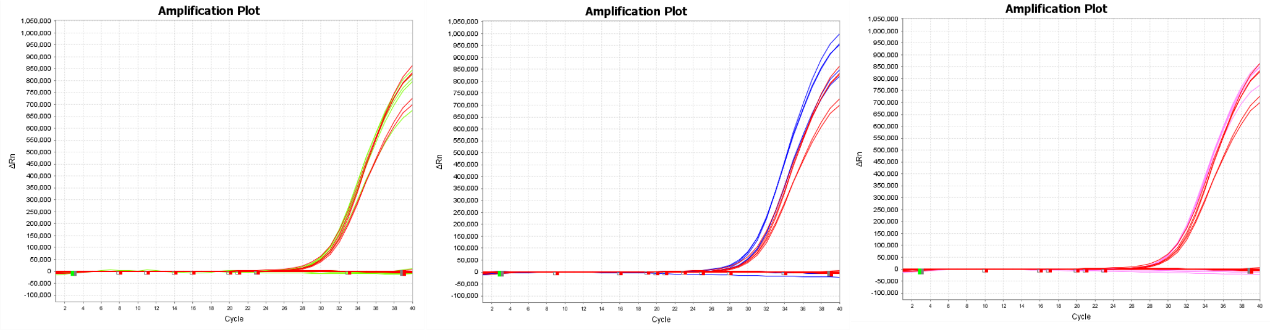
Figure 5 demonstrates that repeated freezing and thawing of reagent 13755 ten times has no influence on its amplification and blocking properties.
Its amplification and blocking effects are unaffected by 37 °C for 7 days.
Experiment: Red: -20°C; Green & Purple: 37°C for 7 days.
Site:L858R
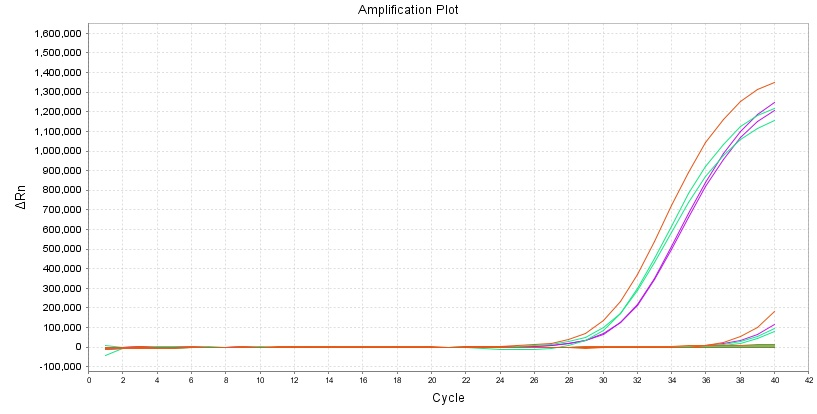
Figure 6 demonstrates that seven days at 37°C have no influence on the amplification and blocking action of 13755 reagent.
5. How do people order products?
Yeasen Biotechnology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., founded in 2014, is a high-tech enterprise engaged in the R &D and production of tool enzyme raw materials and antigen antibodies. Its products include molecular diagnostic enzymes, proteins, and antibodies used in pharmaceuticals, food safety testing, breeding, justice, and other industries. We are committed to providing customers in the field of life sciences with high-quality products and services.The products that Yeasen can provide are as follows:
Table 1: Products provided by Yeasen
|
Product name |
Cat# |
Size |
|
2×Hieff UniconTM Multiplex ARMS qPCR Mix (Inquire) |
13755ES60 |
100T |
|
13755ES80 |
1000T |
|
|
13755ES92 |
10000T |
