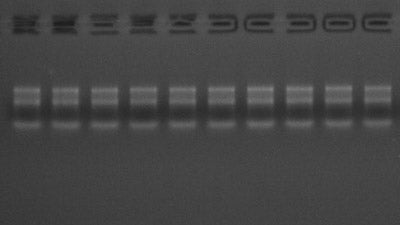
Description
MolPure Cell /Tissue Total RNA Kit was performed by using MolPure DNA removing / RNA binding column technology and new solution systems suitable for extracting high purity and quality total RNA from a variety of fresh or frozen animal tissues or cultured cells. The extraction process does not require toxic phenol, chloroform, β -mercaptoethanol, or precipitation of isopropanol and ethanol. Easy to operate, 15 min to complete the animal tissue or cells (10-30 mg animal tissue or (1-10) ×106 Animal cells) of total RNA extraction. The total RNA is of high purity and can be used in various molecular biology experiments including RT-PCR, qPCR, molecular cloning and RNase protection analysis.
Components
| No. | Name | 19221ES50 (50 T) |
| 19221-A | MolPure DNA removing/RNA binding Column A | 100 |
| 19221-B | 2 mL Collection Tube A2 | 100 |
| 19221-C | Lysate buffer LB(LB Buffer A2) | 30 mL |
| 19221-D | Deproteinized buffer PL (PL Buffer A 2) | 40 mL |
| 19221-E | Wash Buffer W*(Wash Buffer A 2*) | 13 mL |
| 19221-F | RNase-free H2O | 5 mL |
Shipping and Storage
This product should be Store at room temperature, protected from light, for 24 months. 2-8℃lasts longer.
Precautions
Avoid exposing the reagent to air for a long time, which may cause volatilization, oxidation, and changes in pH value. After using each solution, tighten the lid in time.
Observe whether there is precipitation or turbidity in each solution (especially in low-temperature environments such as winter at room temperature), and heat at 37℃ to redissolve the solution to avoid affecting the use effect.
For your safety and health, please wear a lab coat and disposable gloves to operate.
This product is for research use only!
[2] Wang T, Yang J, Lin G, et al. Effects of Dietary Mannan Oligosaccharides on Non-Specific Immunity, Intestinal Health, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Front Immunol. 2021;12:772570. Published 2021 Nov 24. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.772570(IF:7.561)
[3] Wang S, Huang J, Liu F, et al. Isosteviol Sodium Exerts Anti-Colitic Effects on BALB/c Mice with Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis Through Metabolic Reprogramming and Immune Response Modulation. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:7107-7130. Published 2021 Dec 20. doi:10.2147/JIR.S344990(IF:6.922)
[4] Wang S, Huang J, Liu F, et al. Isosteviol Sodium Exerts Anti-Colitic Effects on BALB/c Mice with Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis Through Metabolic Reprogramming and Immune Response Modulation. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:7107-7130. Published 2021 Dec 20. doi:10.2147/JIR.S344990(IF:6.922)
[5] Xu M, Yao J, Shi Y, et al. The SRCAP chromatin remodeling complex promotes oxidative metabolism during prenatal heart development. Development. 2021;148(8):dev199026. doi:10.1242/dev.199026(IF:6.868)
[6] Zhang J, Wang H, Yuan C, et al. ITGAL as a Prognostic Biomarker Correlated With Immune Infiltrates in Gastric Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:808212. Published 2022 Mar 24. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.808212(IF:6.684)
[7] Wang S, Huang J, Tan KS, Deng L, Liu F, Tan W. Isosteviol Sodium Ameliorates Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Chronic Colitis through the Regulation of Metabolic Profiling, Macrophage Polarization, and NF-κB Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:4636618. Published 2022 Jan 27. doi:10.1155/2022/4636618(IF:6.543)
[8] Luo Y, Tao T, Tao R, Huang G, Wu S. Single-Cell Transcriptome Comparison of Bladder Cancer Reveals Its Ecosystem. Front Oncol. 2022;12:818147. Published 2022 Feb 21. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.818147(IF:6.244)
[9] Zhan Z, Liu W, Pan L, Bao Y, Yan Z, Hong L. Overabundance of Veillonella parvula promotes intestinal inflammation by activating macrophages via LPS-TLR4 pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):251. Published 2022 May 6. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-01015-3(IF:5.241)
[10] Feng M, Wang D, Wang X, Yang Y, Zhang S. Bai-Hu-Tang regulates endothelin-1 and its signalling pathway in vascular endothelial cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;284:114812. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114812(IF:4.360)
[11] Zhan Z, Wang Z, Bao Y, Liu W, Hong L. OI inhibits development of ovarian cancer by blocking crosstalk between cancer cells and macrophages via HIF-1α pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;606:142-148. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.03.106(IF:3.575)
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Inquiry
You may also like
FAQ
The product is for research purposes only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic use in humans or animals. Products and content are protected by patents, trademarks, and copyrights owned by Yeasen Biotechnology. Trademark symbols indicate the country of origin, not necessarily registration in all regions.
Certain applications may require additional third-party intellectual property rights.
Yeasen is dedicated to ethical science, believing our research should address critical questions while ensuring safety and ethical standards.