Direct PCR, No Extraction
Direct PCR is a reaction that directly uses blood, animal or plant tissue, etc., for amplification without steps for nucleic acid extraction and nucleic acid purification. It brings unprecedented convenience to DNA amplification, which can save a lot of time. So what are the reagents and products used in direct PCR?
1. What is direct PCR
2. What reagents are needed for direct PCR
3. Application scenarios and characteristics of Direct PCR Kit
4. Product Data
5. Client Feedback
6. Product Ordering Information
1. What is direct PCR
After continuous supplementation and improvement by countless scholars around the world, PCR technology has become the most widely used, most frequently used, and most important basic research method in the entire life science field. Touch Down PCR, RT-PCR, Real-Time PCR, Multi PCR, etc. developed based on the wide application of traditional PCR technology, as well as the latest Digital PCR (Digital PCR), have greatly enriched the research of the majority of scientific researchers. These methods have greatly accelerated the development of modern life sciences, especially molecular biology, and made great contributions to the research of life and nature for the whole human being. Traditional PCR technology and various new technologies and new applications derived from it have a prerequisite, that is, high-purity nucleic acid templates need to be obtained in advance. Any biological sample needs to go through a series of complex and tedious sample processing to obtain nucleic acid samples that meet the technical requirements of PCR. The separation and extraction of DNA and RNA have always been the basic work that relevant scientific and technical personnel need to repeat every day. Due to the huge difference between samples, the separation and extraction process of DNA and RNA is also very different. This work requires a high level of technical proficiency for operators. Due to the use of some highly toxic chemical reagents in the traditional separation and extraction technology, long-term exposure will cause irreversible damage to the operator's body, and even cause direct damage during the experiment. Chemical reagents such as phenol and chloroform are important carcinogens in the laboratory, and the liquid nitrogen used in the process of nucleic acid separation and extraction of plant tissues poses a greater threat to the safety of operators during the experiment due to its ultra-low temperature. At the same time, for those who have a large number of samples to study, separating and extracting nucleic acids is a labor-intensive task. Now the nucleic acid isolation and extraction kits on the market are mature and there are many brands, but they are all roughly the same. Whether it is a silica membrane column centrifugal kit or a magnetic bead method kit, a lot of time is required and the cost is high. In addition to the cost of the kit, there are special requirements for laboratory equipment. The automated workstation used in the magnetic bead method is a very typical large-scale high-value equipment, which is a huge expense for the laboratory. To sum up, before performing PCR experiments, sample pretreatment is an unavoidable and constant headache for researchers. How to solve this problem and directly perform PCR experiments without separation and extraction of nucleic acids has always been a problem that many scientific researchers and clinical laboratory personnel have been thinking about.
Direct PCR is a reaction in which animal or plant tissues are directly used for amplification without nucleic acid extraction. In many ways, direct PCR works like conventional PCR. The main difference is the custom buffer used in direct PCR. The sample can be directly subjected to PCR reaction without nucleic acid extraction, but there are corresponding requirements for the tolerance of the enzymes involved in the direct PCR reaction and the compatibility of the buffer. Although there are more or fewer PCR inhibitors in common samples, direct PCR can still achieve reliable amplification under the action of enzymes and buffers. However, the traditional PCR reaction needs to use high-quality nucleic acid as a template for the reaction. If the template contains proteins and other impurities, it will inhibit the smooth progress of the PCR reaction.
The earliest application field of direct PCR is the field of animals and plants, such as blood, tissue, and hair of mice, cats, chickens, rabbits, sheep, cattle, and other animals; leaves and seeds of plants, etc. It is used to study genotyping, transgenic, plasmid detection, gene knockout analysis, DNA source identification, species identification, SNP analysis, and other fields. These fields have some common characteristics, that is, the content of the target gene is relatively high, and nucleic acid extraction is troublesome. Therefore, direct PCR can not only save time and have little impact on the results, but also save costs.
2. What reagents are needed for direct PCR
2.1 Sample lysate
The sample lysate can be prepared by yourself or purchased. The difference in the components of different brands of lysate will cause the lysing ability to be different, and then the lysing time will be slightly different. For example, for the preparation of animal tissue samples, it is generally recommended to lyse for 30 minutes or overnight, and the lysate for viruses ranges from 3-10 minutes.
2.2 PCR master mix
It is recommended to use a hot-start DNA polymerase to enhance specific amplification and stronger amplification ability. At the heart of direct PCR is a highly resistant polymerase.
2.3 Remove or inhibit components in samples that affect DNA amplification
After the sample is processed by the lysate, proteins, lipids and other cell debris will be released, and these substances will inhibit the PCR reaction. Therefore, direct PCR needs to add corresponding removal or inhibitors to reduce the influence of these factors.
3. Application scenarios and characteristics of Direct PCR Kit
Direct PCR Kit from Yeasen can directly amplify the samples of the plant, animal tissue or blood, and other original samples without nucleic acid purification, which greatly simplifies the PCR experimental process. PCR-based Genotyping (Figure 1) was performed using the original sample without genome purification (Figure 1A) or using its lysate (Figure 1B) as a template. Compared with general PCR-based Genotyping, the direct PCR kit has less sample consumption, simple operation, low experimental cost, and high-quality quantitative sample detection.
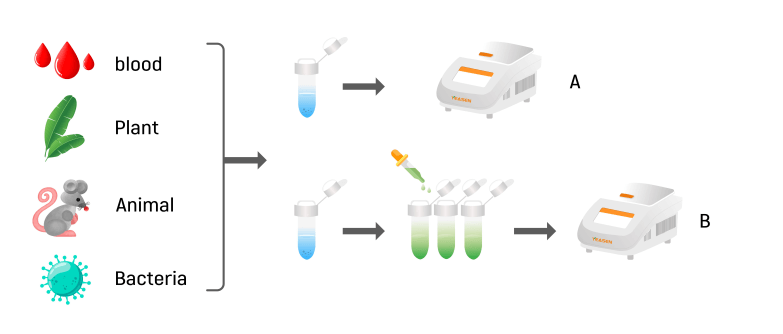
Figure 1. Direct PCR technology.
A. Direct method: Take a small number of samples and directly add them to the PCR Mix for PCR identification. B. Lysis method: Add the sample to the lysis solution to release the genome, and add a small amount of the lysis supernatant to the PCR Mix for PCR identification.
3.1 Applications
Animal gene amplification detection, transgenic animal genotyping, transgenic plant identification, plant genotyping, etc.
3.2 Features
★ Direct: no DNA purification;
★ Fast: 10 min to complete template preparation, 50 min to complete PCR reaction;
★ Simple: Samples can be lysed without shearing or grinding;
PCR Mix is in the form of a master mix, which reduces sample addition steps
★ Saving: less material consumption
★ High throughput: lysis reaction can be completed in 96-well plate
★ Strong inhibitor tolerance
4. Product Data
4.1 Multi-animal universal type: Animal Tissue Direct PCR Kit
4.1.1 Fastest: shorten operation time
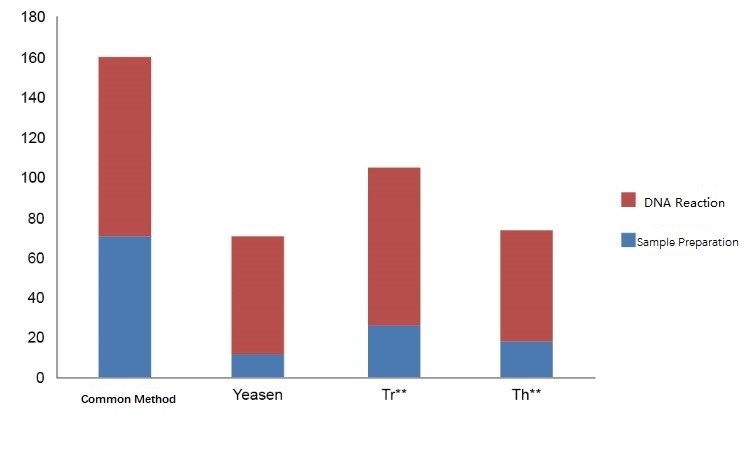
Figure 2. An animal tissue direct PCR kit from Yeasen could save more time.
4.1.2 Example: Genotype Identification of Knockout Mice
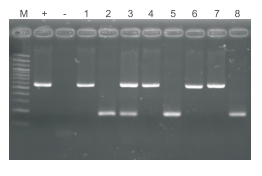
Figure 3. The results of direct amplification of animal tissue direct PCR kit for detection of gene knockout animals.
M: 100bp DNA ladder. Lanes 1-8: lysate as the template. +: 50 ng Purified genomic DNA as the template. ﹣: Deionized water as the template. Several cycles: 35 cycles. Single fragment (580bp): Knockout animal homozygous genome. Single fragment (180bp): Wild-type genome. Two fragments (580bp/180bp): Knockout animal heterozygous genome.
4.2 Rodent-specific: Mouse Tissue Direct PCR Kit
4.2.1 Faster: Sufficient gene release
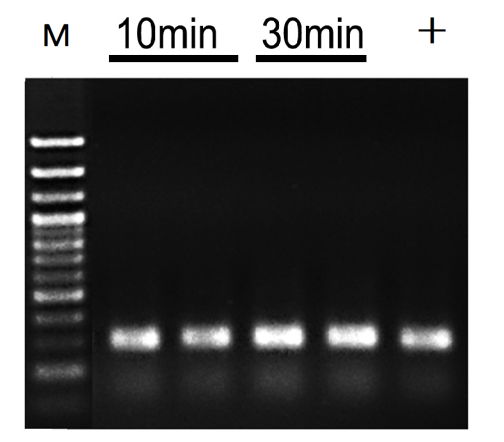
Figure 4 Direct amplification results of mouse tissue direct PCR kit with different lysis times.
M: 100bp DNA ladder. +: 50 ng purified genomic DNA as the template. Several cycles: 35 cycles.
4.2.2 Better than the general alkaline lysis method
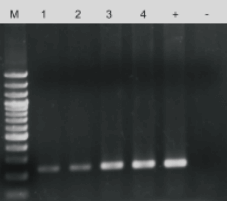
Figure 5. SOX21 gene amplification results of mouse tail treated with different lysis methods.
M: 100 bp DNA ladder. Lanes 1-2: Lysate as a template by general alkaline lysis. Lanes 3-4: Lysate as a template by mouse tissue direct PCR kit. +: 50 ng purified genomic DNA as a template. -: Deionized water as a template. Several cycles: 35 cycles.
4.2.3 Compare with similar products
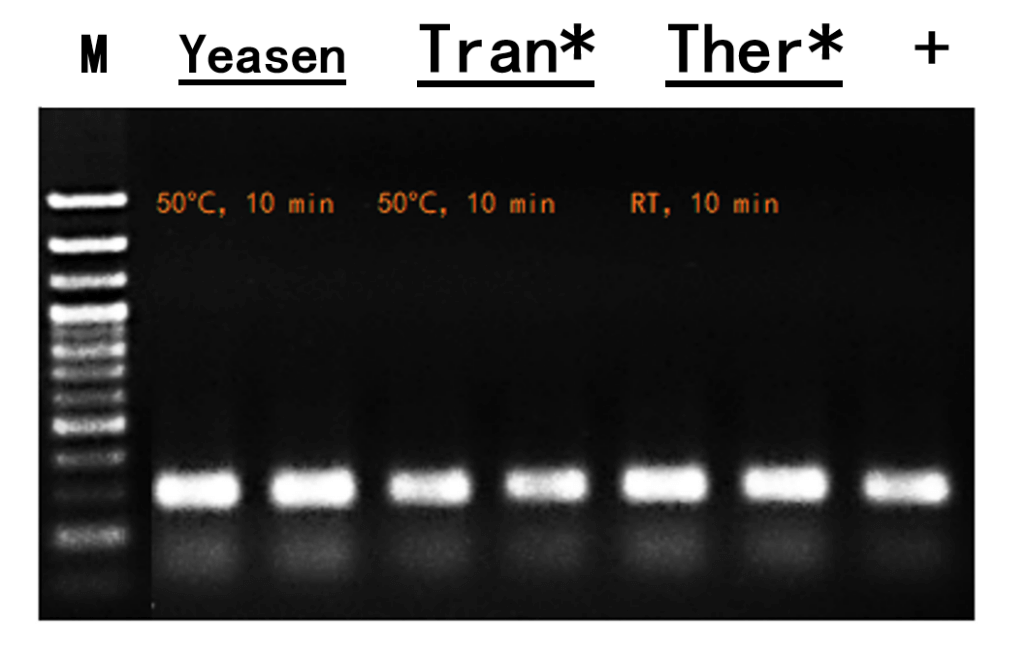
Figure 6. SOX21 gene amplification results of mouse tail treated with similar products from different brands.
M: 100 bp DNA ladder. +: 50 ng purified genomic DNA as the template. Several cycles: 35 cycles.
4.3 Plant Tissue Direct PCR Kit
4.3.1 Multi-type plant sample verification
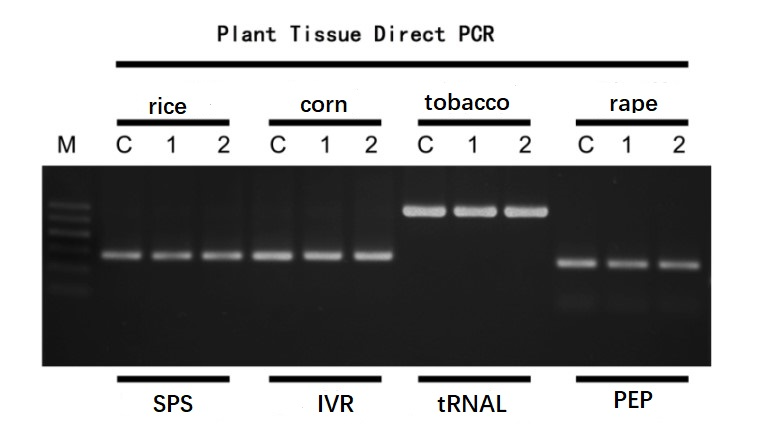
Figure 7. Results of direct amplification of leaves from different plants.
M: 100 bp DNA ladder. C: The purified genomic DNA as a template. Lanes 1-2: The leaf tissue lysate as the template. Several cycles: 30 cycles.
5. Client Feedback
5.1 Mice Genotyping
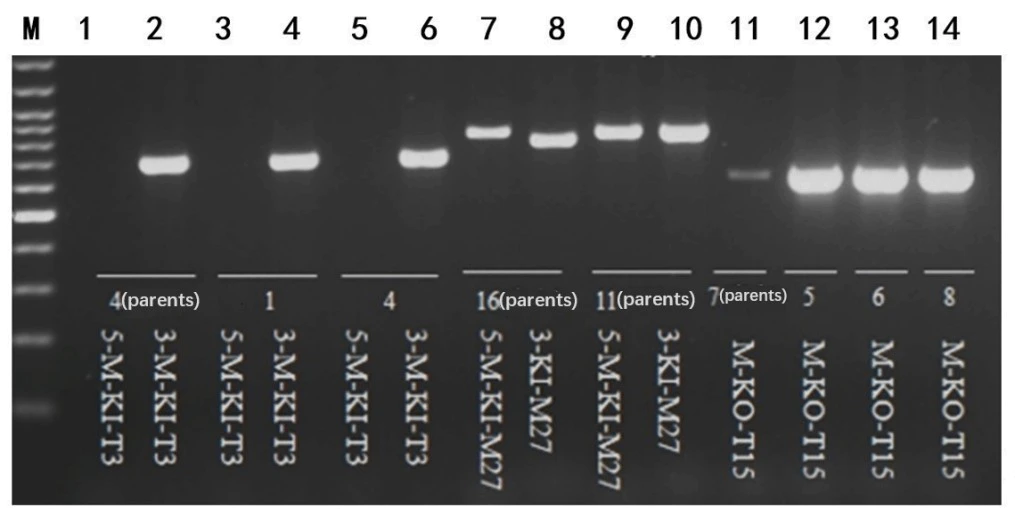
Figure 8. The results of mouse genotype identification using mouse tissue direct PCR kit by users from Beijing Jishi Life Technology Co., Ltd.
5.2 Rice Direct PCR
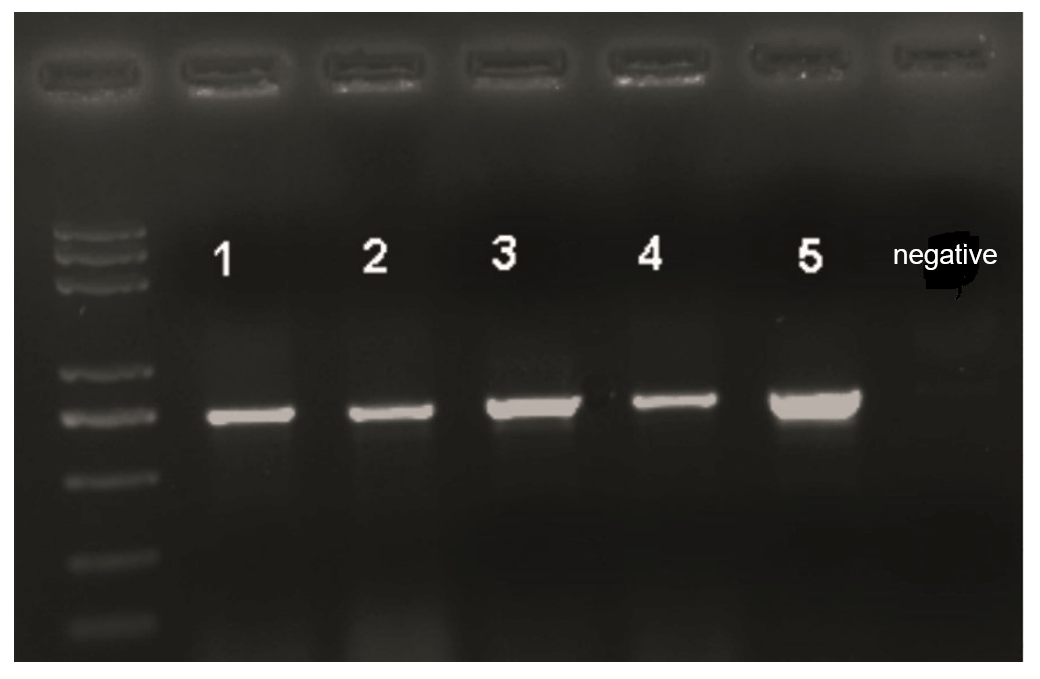
Figure 9. Amplification of rice-related genes using plant tissue direct PCR kits by users of Huazhong Agricultural University.
6. Product Ordering Information
Yeasen is a biotechnology company engaged in the research, development, production, and sales of three major biological reagents: molecules, proteins, and cells. The products provided by Yeasen are as follows.
Table 1. Product Ordering Information
|
Product Name |
Cat# |
Size |
| 2× Hieff™ Ultra-Rapid II HotStart PCR Master Mix (Colony Direct PCR) | 10167ES | 1mL/5mL |
| Mouse Tissue Direct PCR Kit (With Dye) | 10185ES | 50T/200T |
| Plant Tissue Direct PCR Kit (With Dye) | 10187ES | 50T/200T |
| Blood Advanced Direct PCR Kit (With Dye) | 10188ES | 20/50/100/500T |
| Mouse Tissue/ Cell Lysis Reagent | 19697ES | 50T/200T |
